Human Anatomy & Physiology Laboratory Manual Cat Version 13th Edition is a comprehensive and visually engaging guide that introduces students to the structure and function of the human body. Through detailed descriptions, clear illustrations, and hands-on laboratory exercises, this manual provides a solid foundation for understanding human anatomy and physiology.
The manual begins by defining human anatomy and physiology and explaining their importance in understanding human health and disease. It then provides an overview of the different systems of the human body, including the skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems.
Introduction
Human anatomy and physiology are two closely related disciplines that study the structure and function of the human body. Anatomy is the study of the physical structure of the body, while physiology is the study of how the body functions.
The study of human anatomy and physiology is important for a number of reasons. First, it provides us with a basic understanding of how our bodies work. This knowledge can help us to make informed decisions about our health and well-being.
Second, the study of human anatomy and physiology can help us to understand the causes and treatments of disease. Third, the study of human anatomy and physiology can help us to appreciate the complexity and beauty of the human body.
Systems of the Human Body
The human body is made up of a number of different systems, each of which has a specific function. These systems include the skeletal system, the muscular system, the nervous system, the endocrine system, the cardiovascular system, the respiratory system, the digestive system, the urinary system, and the reproductive system.
Laboratory Techniques
Microscopy
Microscopy is a technique used to view small objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye. Microscopes use lenses to magnify objects, making them appear larger and easier to see.
There are two main types of microscopes: light microscopes and electron microscopes. Light microscopes use visible light to illuminate objects, while electron microscopes use a beam of electrons. Electron microscopes can magnify objects much more than light microscopes, but they are also much more expensive.
Dissection
Dissection is a technique used to study the internal structure of an organism. Dissection involves cutting open an organism and examining its internal organs.
Dissection can be used to study a variety of organisms, including humans, animals, and plants. Dissection can provide valuable information about the anatomy and physiology of an organism.
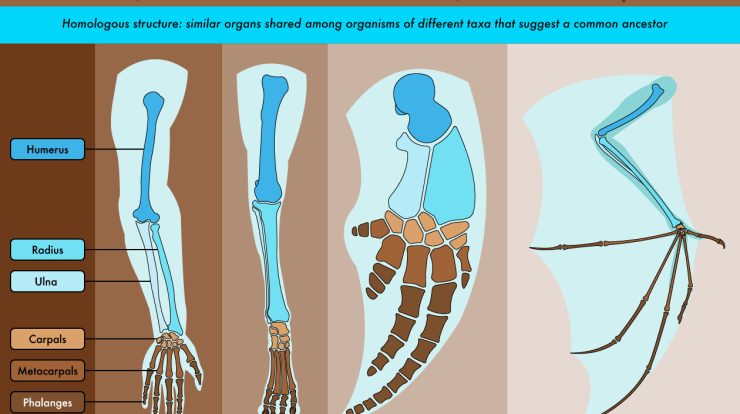
The Skeletal System
The skeletal system is made up of bones, which provide support and protection for the body. The skeletal system also helps to move the body and store minerals.
There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones are divided into two main types: axial bones and appendicular bones. Axial bones are the bones of the head, neck, and trunk. Appendicular bones are the bones of the limbs.
Functions of the Skeletal System, Human anatomy & physiology laboratory manual cat version 13th edition
- Support
- Protection
- Movement
- Mineral storage
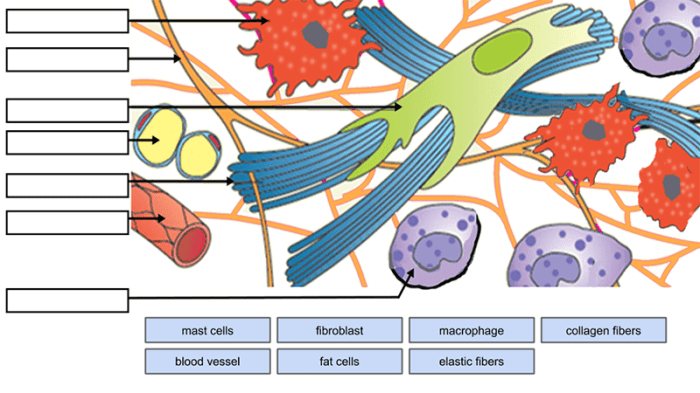
The Muscular System
The muscular system is made up of muscles, which allow the body to move. Muscles are attached to bones and contract to move the bones.
There are three types of muscles in the human body: skeletal muscles, smooth muscles, and cardiac muscles. Skeletal muscles are attached to bones and are responsible for voluntary movement. Smooth muscles are found in the walls of organs and are responsible for involuntary movement.
Cardiac muscles are found in the heart and are responsible for pumping blood.
Functions of the Muscular System
- Movement
- Heat production
- Protection
- Posture
The Nervous System
The nervous system is made up of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. The nervous system controls all of the body’s functions, including movement, sensation, and thought.
The brain is the control center of the nervous system. The brain receives information from the senses and sends signals to the muscles and organs.
Functions of the Nervous System
- Control of movement
- Sensation
- Thought
- Memory
- Emotion
The Endocrine System
The endocrine system is made up of glands that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemical messengers that travel through the bloodstream and control a variety of body functions.
The endocrine system is responsible for regulating a variety of body functions, including growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
Functions of the Endocrine System
- Regulation of growth
- Regulation of metabolism
- Regulation of reproduction
- Regulation of fluid and electrolyte balance
The Cardiovascular System

The cardiovascular system is made up of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The cardiovascular system is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body.
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood through the blood vessels. The blood vessels are a network of tubes that carry blood throughout the body.
Functions of the Cardiovascular System
- Pumping blood throughout the body
- Transporting oxygen and nutrients to the cells
- Removing waste products from the cells
- Regulating body temperature
The Respiratory System: Human Anatomy & Physiology Laboratory Manual Cat Version 13th Edition

The respiratory system is made up of the lungs and the airways. The respiratory system is responsible for bringing oxygen into the body and removing carbon dioxide.
The lungs are two large organs that are located in the chest. The lungs are filled with air sacs called alveoli. The alveoli are where gas exchange occurs.
Functions of the Respiratory System
- Bringing oxygen into the body
- Removing carbon dioxide from the body
- Regulating blood pH
The Digestive System
The digestive system is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and rectum. The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food and absorbing nutrients.
The mouth is where food is chewed and mixed with saliva. The saliva contains enzymes that begin to break down the food.
Functions of the Digestive System
- Breaking down food
- Absorbing nutrients
- Eliminating waste products
The Urinary System
The urinary system is made up of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The urinary system is responsible for filtering waste products from the blood and producing urine.
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs that are located in the back of the abdomen. The kidneys filter waste products from the blood and produce urine.
Functions of the Urinary System
- Filtering waste products from the blood
- Producing urine
- Regulating blood volume
- Regulating blood pH
The Reproductive System
The reproductive system is made up of the organs that are responsible for producing offspring. In males, the reproductive system includes the testes, epididymides, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and penis. In females, the reproductive system includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina.
The testes are two small organs that are located in the scrotum. The testes produce sperm.
Functions of the Reproductive System
- Producing offspring
- Secreting hormones
Essential Questionnaire
What is the purpose of Human Anatomy & Physiology Laboratory Manual Cat Version 13th Edition?
Human Anatomy & Physiology Laboratory Manual Cat Version 13th Edition is a comprehensive guide that introduces students to the structure and function of the human body through detailed descriptions, clear illustrations, and hands-on laboratory exercises.
What are the key features of Human Anatomy & Physiology Laboratory Manual Cat Version 13th Edition?
The key features of Human Anatomy & Physiology Laboratory Manual Cat Version 13th Edition include clear and concise explanations, detailed illustrations, engaging laboratory exercises, and a comprehensive glossary of terms.
Who is the intended audience for Human Anatomy & Physiology Laboratory Manual Cat Version 13th Edition?
Human Anatomy & Physiology Laboratory Manual Cat Version 13th Edition is intended for students studying human anatomy and physiology.